dom lizarraga
Rails code guide through with Kasper Timm Hansen | notes
Next session with Kasper (luma link)
Last Friday I attended a session with Kasper where he shared with us how he usually explores Rails codebase, he’s got a lot of experience doing this therefore I applied what I learned here.
I’ve always been curious how callbacks and model validations work in Rails, so I decided to explore this topic.
- Setting up the app
- Possible error with bundle
- First exploration with ActiveRecord lib
superkeyword for.valid?superkeyword for.save- Ruby call stack
- Recap with flow chart
- Shortcut for Ruby method lookup
Always have a question in mind that you want to answer otherwise it may be pretty easy to get lost.💡
Setting up the app
# create a new rails app
rails new callbacks && cd callbacks
# create a new model
rails g model Post title
rails db:migrate
# add the following code to the model
class Post < ApplicationRecord
validates :title, presence: true, allow_nil: false
before_validation :titleize_title
after_create :print_out_title
private
def titleize_title
return unless title.present?
self.title = title.downcase.titleize
puts "before_validation- Title changed to #{title}"
end
def print_out_title
puts "after_create- Title was saved as: #{title}"
end
end
After setting up a very basic app with 2 callbacks, and one validation, we can see that both callbacks are running corrrectly.
➜ callbacks git:(main) ✗ rc
Loading development environment (Rails 8.0.1)
callbacks(dev)> p = Post.new
=> #<Post:0x00000001205322c8 id: nil, title: nil, created_at: nil, updated_at: nil>
callbacks(dev)> p.valid?
=> false
callbacks(dev)> p.errors.full_messages
=> ["Title can't be blank"]
callbacks(dev)> p.title = "HOLA"
=> "HOLA"
callbacks(dev)> p.save
before_validation- Title changed to Hola 👈
TRANSACTION (0.1ms) BEGIN immediate TRANSACTION /*application='Callbacks'*/
Post Create (10.0ms) INSERT INTO "posts" ("title", "created_at", "updated_at") VALUES ('Hola', '2025-02-03 01:09:45.881379', '2025-02-03 01:09:45.881379') RETURNING "id" /*application='Callbacks'*/
after_create- Title was saved as: Hola 👈
TRANSACTION (0.3ms) COMMIT TRANSACTION /*application='Callbacks'*/
=> true
Pretty standard, now what does trigger ‘active_record_callbacks’? Was it after calling “.valid?” or “.save”?
Possible error with bundle
Let’s go and open active_record library with ‘bundle open activerecord’, it might throw you an error, I fixed it by typing:
# in your console, it will work for one session
EDITOR=code bundle open activerecord
# or permanently set it in your .zshrc file
export BUNDLER_EDITOR=code
# close the .zshrc file
source ~/.zshrc
Docs for ‘bundle open’ and setting your editor for opening gems 🪄
First exploration with ActiveRecord lib
Within lib/active_record/validations.rb:69 and after reading a bit we can see the following chain of method calls:
save → perform_validations → valid?.
Let’s add a puts statement and test it out.
def valid?(context = nil)
puts "you are calling 'valid?' :)" # added for testing 👈
context ||= default_validation_context
output = super(context) # <--- calls ActiveModel::Validations#valid? (parent method)
errors.empty? && output
end
Close the editor and ‘reload!’ rails console
➜ callbacks git:(main) reload!
Loading development environment (Rails 8.0.1)
callbacks(dev)> p = Post.new
=> #<Post:0x0000000120b394c8 id: nil, title: nil, created_at: nil, updated_at: nil>
callbacks(dev)> p.valid?
you are calling 'valid?' :) 👈
=> false
callbacks(dev)> p.title = "HOLA!"
=> "HOLA!"
callbacks(dev)> p.save
you are calling 'valid?' :) 👈
before_validation- Title changed to Hola!
TRANSACTION (0.1ms) BEGIN immediate TRANSACTION /*application='Callbacks'*/
Post Create (3.0ms) INSERT INTO "posts" ("title", "created_at", "updated_at") VALUES ('Hola!', '2025-02-03 01:32:16.234929', '2025-02-03 01:32:16.234929') RETURNING "id" /*application='Callbacks'*/
after_create- Title was saved as: Hola!
TRANSACTION (0.5ms) COMMIT TRANSACTION /*application='Callbacks'*/
=> true
We can conclude with this inspection that each time we call “.save” or “save!” we call in the end “.valid?”.
Now, let’s explore the 2 ‘super’ keywords following the chain of methods up to its ancestor.
‘super’ keyword for .valid?
Let’s open the gem with ‘bundle open activemodel’.
‘.valid?’ will invoke ActiveModel::Validations#valid? lib/active_model/validations.rb:361 this method will call ‘run_validations!’ which is defined in lib/active_model/validations.rb:459
def valid?(context = nil)
current_context = validation_context
context_for_validation.context = context
errors.clear
run_validations! # <--- calls all validation callbacks (returns true if the record is valid, false otherwise)
ensure
context_for_validation.context = current_context
end
run_validations! → _run_validate_callbacks
The latter comes from ActiveSupport::Callbacks, it is dynamically generated via ‘define_callbacks’, inside of this ActiveSupport module you’ll find very interesting classes as Before, After, Around, CallbackSequence, CallbackChain (where the callbacks are stored in a [])
‘super’ keyword for .save
The second ‘super’ keyword is in ‘.save’ and goes up to ActiveRecord::Persistence module.
Just for making this more practical I have added a puts statement to lib/active_record/persistence.rb:390
def save(**options, &block)
create_or_update(**options, &block)
puts "you saved it :)" # added for testing 👈
rescue ActiveRecord::RecordInvalid
false
end
rails console 🎮
callbacks(dev)> p = Post.new
=> #<Post:0x000000011d5b92a8 id: nil, title: nil, created_at: nil, updated_at: nil>
callbacks(dev)> p.title = "HOLA?"
=> "HOLA?"
callbacks(dev)> p.valid?
you are calling 'valid?' :)
before_validation- Title changed to Hola?
=> true
callbacks(dev)> p.save
you are calling 'valid?' :)
before_validation- Title changed to Hola?
TRANSACTION (0.1ms) BEGIN immediate TRANSACTION /*application='Callbacks'*/
Post Create (8.7ms) INSERT INTO "posts" ("title", "created_at", "updated_at") VALUES ('Hola?', '2025-02-03 23:16:20.758330', '2025-02-03 23:16:20.758330') RETURNING "id" /*application='Callbacks'*/
after_create- Title was saved as: Hola?
you saved it :) 👈
TRANSACTION (0.0ms) ROLLBACK TRANSACTION /*application='Callbacks'*/
=> nil
‘.save’ will call ‘create_or_update’ and then depending on whether the object is new or not, it can be about an ‘insert’ or ‘update’ operation.
How ruby call up its ancestor objects
Something that was difficult to wrap my head around was why ‘valid?’ and ‘save’ point to different modules and how they get overridden? After some lookups I figured that this is because in ‘lib/active_record/base.rb’ we have the following:
Module ActiveRecord
class Base
include Persistence
include Validations
include Callbacks
...
end
end
Since Validations is included after Persistence, it overrides ‘save’, adding validation checks before calling ‘super’ to go back to ‘Persistence#save’.
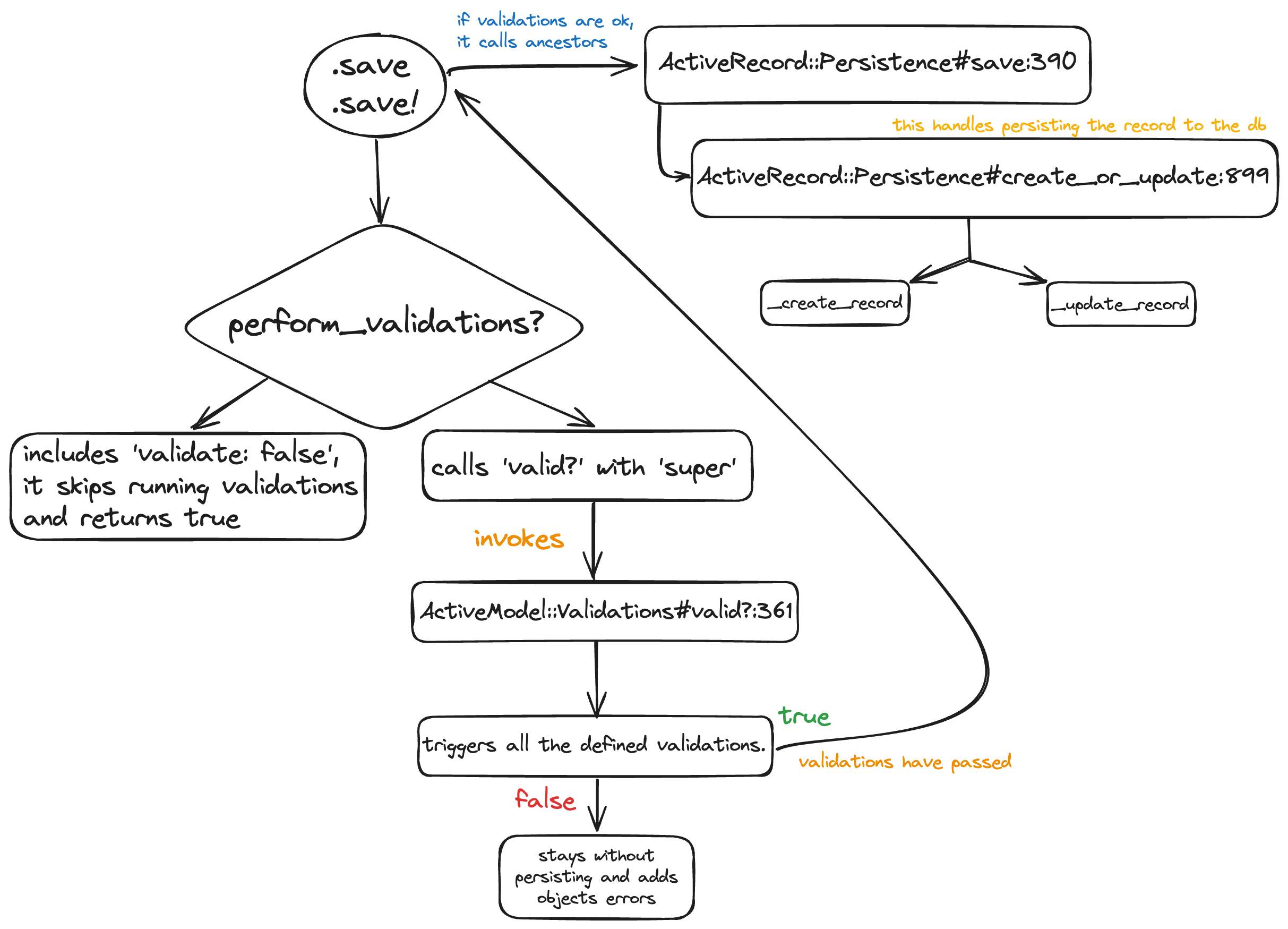
Recap with visual aid
When we call ‘.save’, Ruby follows this lookup order:
First, it checks the model’s own class (Post in this case). The Post model does not define ‘save’, so Ruby looks in the included modules.
If not found, it looks in Callbacks, which does not define ‘save’ either.
Third, it checks ‘ActiveRecord::Validations#save’. Since this method exists, it runs, calling ‘perform_validations’. If validation passes, it calls ‘super’, which means “find the next save method in the lookup chain.”
Finally, super calls ‘ActiveRecord::Persistence#save’. This method handles inserting/updating the record.
↑
Validations
↑
Callbacks
↑
Transactions
↑
First, Ruby looks in the Post class itself
Here a flow chart as recap of what we explored:
Shorcut - Ruby method lookup
I got some feeback from Kasper and he suggested the following commands as alternatives, they seem to be more efficient than looking up the code in the gem.
The code will tell you where the method is defined, and you can keep chaining .super_method to go up the inheritance chain.
➜ callbacks git:(main) rc
Loading development environment (Rails 8.0.1)
callbacks(dev)> Post.instance_method(:save).super_method
=> #<UnboundMethod: ActiveRecord::Transactions#save(**) /Users/dominiclizarraga/.rbenv/versions/3.4.1/lib/ruby/gems/3.4.0/gems/activerecord-8.0.1/lib/active_record/transactions.rb:361>
# 2 times '.super_method'
callbacks(dev)> Post.instance_method(:save).super_method.super_method
=> #<UnboundMethod: ActiveRecord::Validations#save(**options) /Users/dominiclizarraga/.rbenv/versions/3.4.1/lib/ruby/gems/3.4.0/gems/activerecord-8.0.1/lib/active_record/validations.rb:47>
# 3 times '.super_method'
callbacks(dev)> Post.instance_method(:save).super_method.super_method.super_method
=> #<UnboundMethod: ActiveRecord::Persistence#save(**options, &block) /Users/dominiclizarraga/.rbenv/versions/3.4.1/lib/ruby/gems/3.4.0/gems/activerecord-8.0.1/lib/active_record/persistence.rb:390>
And also for seeing the module hierarchy and suplerclasses you can use the following command:
Post.ancestors
=>
[Post (call 'Post.load_schema' to load schema informations),
Post::GeneratedAssociationMethods,
Post::GeneratedAttributeMethods,
ApplicationRecord(abstract),
ApplicationRecord::GeneratedAssociationMethods,
ApplicationRecord::GeneratedAttributeMethods,
ActionText::Encryption,
ActiveRecord::Base,
Turbo::Broadcastable, 🤯
ActionText::Attribute,
ActiveStorage::Reflection::ActiveRecordExtensions,
ActiveStorage::Attached::Model,
GlobalID::Identification,
ActiveRecord::Marshalling::Methods,
...
...
...
ActiveRecord::ReadonlyAttributes,
ActiveRecord::Persistence, 👈
ActiveSupport::Callbacks, 👈
ActiveModel::Validations, 👈
ActiveSupport::Dependencies::RequireDependency,
Object,
PP::ObjectMixin,
ActiveSupport::ToJsonWithActiveSupportEncoder,
ActiveSupport::Tryable,
JSON::Ext::Generator::GeneratorMethods::Object,
Kernel,
BasicObject]